SOFR Swaps
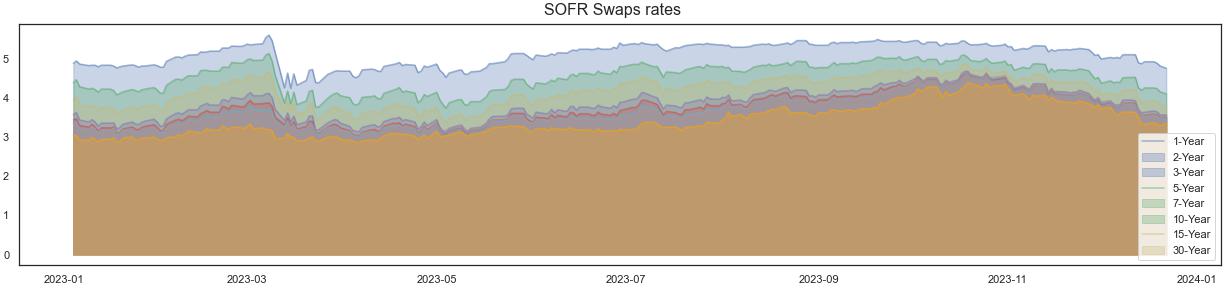
MacroVar monitors SOFR swaps. SOFR swap rates are a common benchmark for pricing fixed-rate loans and fixed-rate CMBS.| SOFR Swap Rates | |
|---|---|
| 1 Year | 0.0528% |
| 2 Years | 0.0477% |
| 3 Years | 0.0448% |
| 5 Years | 0.0423% |
| 7 Years | 0.0416% |
| 10 Years | 0.0414% |
| 15 Years | 0.0417% |
| 30 Years | 0.0394% |
SOFR Swaps Chart
What are SOFR swaps
SOFR stands for the Secured Overnight Financing Rate, which is a benchmark interest rate that serves as an alternative to LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate). SOFR is based on overnight Treasury repurchase agreements and is considered a more robust and transparent benchmark.SOFR is a robust and transparent overnight interest rate, grounded in the vast and liquid U.S. Treasury repurchase agreement (repo) market. Unlike LIBOR, which was susceptible to manipulation and lacked solid foundations during the financial crisis, SOFR is designed to reflect the cost of borrowing on an overnight, collateralized basis.
SOFR swaps are financial derivatives that allow parties to exchange cash flows based on the SOFR rate over a specified period. These swaps are used to manage interest rate risk. For example, a company with variable-rate debt might enter into a SOFR swap to convert its variable-rate payments to fixed-rate payments or vice versa. SOFR swaps are a key component of the transition away from LIBOR, which is being phased out in various currencies due to concerns about its reliability and potential manipulation.
SOFR swap rate is a swap where a counterparty pays a fixed-rate on an annual, Act/360 basis and receives SOFR, reset daily and paid annually on an Act/360 basis. This rate is a common benchmark for pricing fixed-rate CMBS and other fixed-rate loans.
In a plain "vanilla" swap, one party agrees to pay a fixed interest rate, and, in exchange, the receiving party agrees to pay a floating interest rate based on the SOFR—the rate may be higher or lower than SOFR, based on the party's credit rating and interest-rate conditions.
How are SOFR swap rates determined
Each business day, the New York Fed publishes the SOFR on the New York Fed website at approximately 8:00 a.m. ET. For more information on the SOFR's publication schedule and methodology, see Additional Information about Reference Rates Administered by the New York Fed.
Introduction to SOFR Swaps
In the evolving landscape of financial markets, the transition from LIBOR to alternative benchmark rates is a crucial paradigm shift. One prominent player in this transition is the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR). SOFR swaps, a derivative product, play a pivotal role in managing interest rate exposure in this new era.The Purpose of SOFR Swaps
SOFR swaps provide a mechanism for market participants to hedge or speculate on interest rate movements linked to SOFR. These swaps enable parties to exchange cash flows based on the SOFR rate over a predetermined period, allowing them to effectively manage interest rate risk associated with their financial instruments.
Key Features of SOFR Swaps
- Benchmark Transition: SOFR swaps facilitate the transition away from LIBOR, offering a reliable and forward-looking alternative for market participants.
- Cash Flow Exchange: Parties entering into SOFR swaps agree to exchange cash flows based on the difference between fixed and floating SOFR rates. This helps in aligning payment streams with the preferred risk profile of the participants.
- Risk Management: SOFR swaps serve as a valuable tool for entities with exposure to interest rate fluctuations, allowing them to mitigate risks associated with variable-rate debt or investments.
How are SOFR swap rates determined
Each business day, the New York Fed publishes the SOFR on the New York Fed website at approximately 8:00 a.m. ET. For more information on the SOFR's publication schedule and methodology, see Additional Information about Reference Rates Administered by the New York Fed.