Interest Coverage Ratio: A Measure of a Company’s Ability to Pay Its Interest Expenses
The interest coverage ratio, also known as the times interest earned ratio, is a financial metric used to assess a company’s ability to meet its interest payment obligations on its debt. It indicates how well a company’s operating income can cover its interest expenses. In other words, it measures the company’s capacity to make interest payments from its earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT).
The formula for calculating the interest coverage ratio is: Interest Coverage Ratio = EBIT / Interest Expenses
Where:
EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) represents a company’s operating income before deducting interest and taxes.
Interest Expenses refer to the interest payments a company needs to make on its outstanding debt.
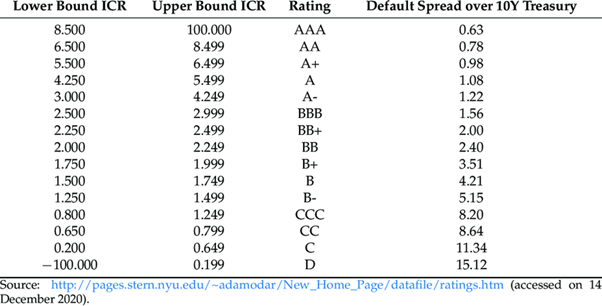
An Interest Coverage Ratio of 2 is commonly regarded as the minimum acceptable level across various industries. However, what the market deems acceptable or not can vary among industries.
Creditors evaluate a company’s operational performance in relation to its capacity to meet its debt obligations when deciding whether to grant new debt. Credit ratings are also influenced by this factor.