Finland Economy
Finland has a mixed economy, which means that it combines elements of both a market economy and a planned economy. The country's economy is driven by a number of different industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, and services.Agriculture is an important part of the Finnish economy, and the country is known for producing a wide range of agricultural products, including grains, fruits, and vegetables. The agricultural sector accounts for a relatively small share of the country's GDP, but it is an important contributor to the economy.
The manufacturing sector is also an important part of the Finnish economy, and the country has a well-developed industrial base. Finland is known for producing a wide range of goods, including machinery, chemicals, and consumer products. The service sector is also a major contributor to the economy, and it includes activities such as finance, insurance, and real estate.
Despite these strengths, the Finnish economy has faced some challenges in recent years. The country has struggled with high unemployment and a large public debt, which has made it difficult to stimulate economic growth. Additionally, the country has experienced periods of political and economic instability, which has made it a less attractive destination for foreign investment.
Overall, the future outlook for the Finnish economy is uncertain, but with the right policies and investments, it has the potential to grow and prosper in the coming years.
The Finnish economy is composed of several different sectors, including agriculture, manufacturing, and services.
Agriculture is an important part of the Finnish economy, and the country is known for producing a wide range of agricultural products, including grains, fruits, and vegetables. The agricultural sector accounts for a relatively small share of the country's GDP, but it is an important contributor to the economy.
The manufacturing sector is also an important part of the Finnish economy, and the country has a well-developed industrial base. Finland is known for producing a wide range of goods, including machinery, chemicals, and consumer products. The service sector is also a major contributor to the economy, and it includes activities such as finance, insurance, and real estate.
Overall, the different sectors of the Finnish economy are interconnected, and each one plays a vital role in driving economic growth and development. Despite some challenges, the country has a strong foundation and a diverse range of industries, which gives it the potential to continue growing and prospering in the future.
Finland macroeconomic model analysis
The two most important economic indicators of the Finland economy are real economic growth expectations and inflation. MacroVar uses Finland Manufacturing ESI Order Books to gauge economic growth expectations and Finland Manufacturing ESI Selling Price expectations of next months to gauge inflation expectations. Finland's economy is healthy when it generates stable economic growth with low inflation. Policymakers (the government and the central bank) use fiscal and monetary policy to inject liquidity during slowdowns (to solve weak economic growth) and withdraw liquidity from an overheating economy (to solve high inflation).
The four economic environments
There are 4 economic environments based on economic growth and inflationary conditions. Financial assets are affected by economic growth and inflation expectations as explained in the diagram below.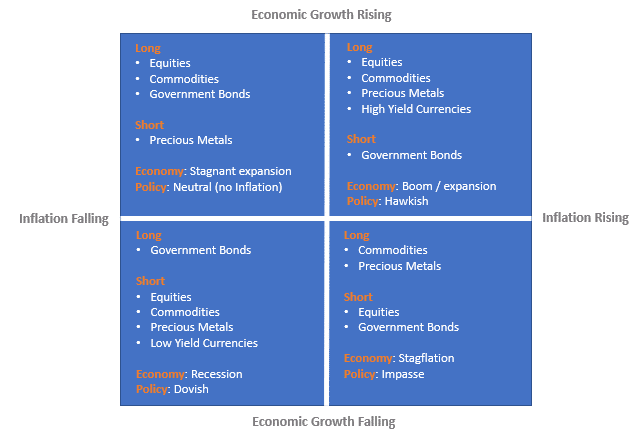
- Inflation boom: Accelerating Economic growth with Rising inflation - Monetary Policy response: Hawkish
- Stagflation: Slowing Economic Growth with Rising Inflation - Monetary Policy response: Dilemma
- Disinflation boom: Accelerating Economic growth with Slowing Inflation - Monetary Policy response: Neutral
- Deflation Bust: : Slowing Economic Growth with Falling Inflation - Monetary Policy response: Dovish