Nigeria Economy & Nigeria Markets Data analytics
MacroVar monitors real-time economic, financial and geopolitical developments for the Nigeria economy and Nigeria markets by analyzing financial, economic data and real-time news using statistical models. To help you forecast and analyze economic and financial developments, our team provides you with explanations of the theory and structure of our models and access to financial and economic data.
Nigeria Overview
Nigeria Overview presents the current trends and dynamics of the major Nigeria financial markets and economic indicators. Select Details to get more information for each indicator, use Factors to monitor current statistical analysis of financial & economic factors affecting the specific asset, and select research to read the latest MacroVar research for the specific asset/indicator.
| Price | 1D% | M | T | B | Factors | Research | Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSE All Share | 99802.1 | 0 | 0.01 | 64.38 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nigeria 2-Year Bond Yield | 23.59 | 15.89 | 0.2 | 203.24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nigeria 10-year bond yield | 19.69 | 0 | 0.01 | 49.44 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nigerian Naira US Dollar (NGN/USD) | 1561.51 | -1.79 | 0.02 | 97.21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| manufacturing pmi | 42.8 | -13 | -13 | -18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Services PMI | 36.2 | -23 | -23 | -23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Price | 1D% | M | T | B | Factors | Research | Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSE All Share | 99802.1 | 0 | 0.01 | 64.38 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nigeria ETF | 3.74 | 0 | 0.02 | -53.69 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nigeria 2-Year Bond Yield | 23.59 | 15.89 | 0.2 | 203.24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nigeria 10-year bond yield | 19.69 | 0 | 0.01 | 49.44 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nigeria Yield Curve | -3.9 | 484.13 | 22.51 | -329.39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nigerian Naira US Dollar (NGN/USD) | 1561.51 | -1.79 | 0.02 | 97.21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Price | 1D% | M | T | B | Factors | Research | Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composite PMI | 36.2 | -23 | -23 | 974 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| manufacturing pmi | 42.8 | -13 | -13 | -18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Services PMI | 36.2 | -23 | -23 | -23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GDP Growth (annual) | 2.98 | -14 | -14 | 484 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unemployment rate | 5 | 19 | 19 | -65 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Price | 1D% | M | T | B | Factors | Research | Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSE All Share | 99802.1 | 0 | 0.01 | 64.38 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nigeria 2-Year Bond Yield | 23.59 | 15.89 | 0.2 | 203.24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nigeria 10-year bond yield | 19.69 | 0 | 0.01 | 49.44 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nigerian Naira US Dollar (NGN/USD) | 1561.51 | -1.79 | 0.02 | 97.21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nigeria Economic Overview
Nigeria economic overview presents a snapshot of Nigeria current economic conditions. You can find details for the Nigeria economy subsections by exploring the sections below.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composite PMI | ng.comppmi | 36.2 | 47.1 | -23 | 974 | UP | UP |
| manufacturing pmi | ng.manpmi | 42.8 | 49.4 | -13 | -18 | Down | Down |
| services pmi | ng.servpmi | 36.2 | 47.1 | -23 | -23 | Down | Down |
Nigeria Manufacturing
MacroVar tracks hundreds of indicators related to Nigeria manufacturing. Our focus is on the most important leading indicators based on the ISM report and related indicators. The ISM report is the most important report reflecting the real demand of goods in the Nigeria economy.
| 1Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| manufacturing pmi | ng.manpmi | 42.8 | 49.4 | -13 | -18 | Down | Down |
| industrial production | ng.indproduction | -9.7 | 15.2 | -164 | -385 | Down | Down |
Nigeria Services
MacroVar tracks hundreds of indicators related to Nigeria services. Our focus is on the most important leading indicators based on the ISM report and related indicators. The ISM report is the most important report reflecting the real demand of services in the Nigeria economy.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| services pmi | ng.servpmi | 36.2 | 47.1 | -23 | -23 | Down | Down |
Nigeria consumer sentiment
Consumer spending makes up 67% of the U.S. Economy. MacroVar monitors direct consumer reports like the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index and indirect macroeconomic indicators related to Nigeria employment and Nigeria consumer activity (building permits).
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| consumer confidence | ng.consconfidence | -14.8 | -21.2s | -30 | -1580 | Down | Down |
| unemployment rate | ng.unemploymentrate | 5.0 | 4.2s | 19 | -65 | Down | Down |
Nigeria Construction
The Nigeria construction sector is a significant component of the Nigeria economy. MacroVar monitors leading indicators of construction activity like building permits and new home sales.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|
Nigeria Macroeconomic outlook
Nigeria Macroeconomic outlook presents an overview of the long-term fundamental coincident factors of the Nigeria economy. Components monitored are the country's rserves, debt, Monetary Policy and Fiscal Policy. Explore Nigeria macroeconomic model in detail.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gdp | ng.gdp | 362.81 | 472.62 | -23 | -12 | Down | Down |
| Real GDP | ng.realgdp | 18278213.01 | 21773300 | -16 | 9 | Down | UP |
| gdp growth annual | ng.gdpgrowthan | 2.98 | 3.46 | -14 | 484 | Down | UP |
| gdp growth | ng.gdpgrowth | -16.1 | 12 | -234 | -245 | Down | Down |
| interest rate | ng.interestrate | 26.25 | 24.75 | 6 | 42 | UP | UP |
| unemployment rate | ng.unemploymentrate | 5.0 | 4.2 | 19 | -65 | Down | Down |
| external debt | ng.externaldebt | 41594.52 | 43159.2 | -4 | 30 | UP | UP |
| government debt to gdp | ng.govdebtgdp | 38.8 | 38 | 2 | 88 | UP | UP |
| current account | ng.currentaccount | 3280.0 | 2870 | 14 | -191 | UP | UP |
| current account to gdp | ng.currentaccountgdp | -0.3 | -0.3 | 0 | -110 | Down | Down |
| exports | ng.exports | 4284566.61 | 4267980 | 0 | 123 | UP | UP |
| imports | ng.imports | 4104729.0 | 4822310 | -15 | 120 | UP | UP |
| foreign exchange reserves | ng.fxreserves | 34070.0 | 32690 | 4 | -0 | UP | Down |
| gold reserves | ng.goldres | 21.37 | 21.37 | 0 | -0 | Down | Down |
| government revenues | ng.govrev | 1693.02 | 1510.09 | 12 | 89 | UP | UP |
| fiscal expenditure | ng.fiscalexp | 4040.18 | 4175.35 | -3 | 90 | UP | UP |
Nigeria Inflation
MacroVar monitors major inflation indexes and subcompoonents based on Bureau of Labour Statistics monthly report.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| core inflation rate | ng.coreinflationrate | 27.4 | 27.04 | 1 | 35 | 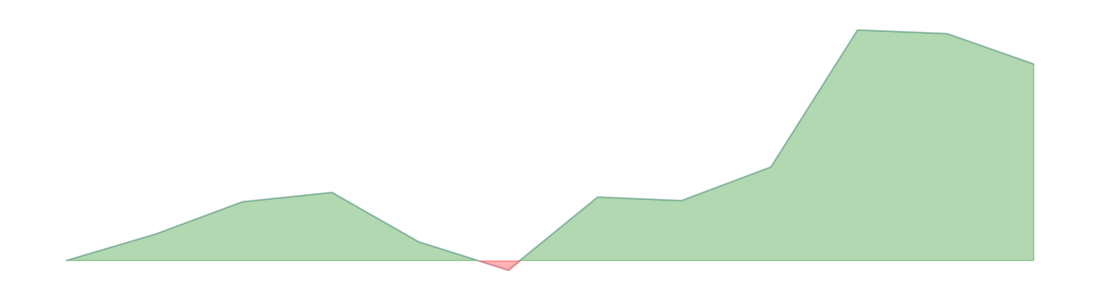 |
Nigeria Employment
MacroVar monitors leading indicators (ISM/NMI employment activity), coincident (Initial & Continuing jobless claims) and lagging indicators of Nigeria employment. Nigeria employment is one of the major factors affecting Nigeria monetary policy.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unemployment rate | ng.unemploymentrate | 5.0 | 4.2 | 19 | -65 | Down | Down |
Nigeria Monetary Policy
Nigeria Monetary policy is monitored by tracking the most important indicators related to the Fed's balance sheet and interest rates.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| interest rate | ng.interestrate | 26.25 | 24.75 | 6 | 42 | UP | UP |
| money supply m1 | ng.msm1 | 33382632.88 | 33819000 | -1 | 48 | UP | UP |
| money supply m2 | ng.msm2 | 98986356.49 | 96963500 | 2 | 78 | UP | UP |
| government debt to gdp | ng.govdebtgdp | 38.8 | 38 | 2 | 88 | UP | UP |
| Nigeria Credit Rating (S&P) | RATING.S&P.NG | ||||||
| Nigeria Credit Rating (Moody's) | RATING.MOODYS.NG | ||||||
| Nigeria Credit Rating (Fitch) | RATING.FITCH.NG |
Nigeria Fiscal Policy
Nigeria Fiscal policy is monitored by tracking the most important indicators related to the Treasury's decisions on government spending, revenues and budget surplus/deficit.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| government revenues | ng.govrev | 1693.02 | 1510.09 | 12 | 89 | UP | UP |
| fiscal expenditure | ng.fiscalexp | 4040.18 | 4175.35 | -3 | 90 | UP | UP |
| government budget | ng.govbudget | -6.1 | -5 | 22 | 336 | Down | Down |
| Government budget | ng.govbudgetvalue | -2347.16 | -2665.26 | -12 | 88 | Down | Down |
| government debt to gdp | ng.govdebtgdp | 38.8 | 38 | 2 | 88 | UP | UP |
Nigeria Trade
Nigeria trade activity is monitored by tracking Trade and Capital flows.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current account | ng.currentaccount | 3280.0 | 2870 | 14 | -191 | UP | UP |
| current account to gdp | ng.currentaccountgdp | -0.3 | -0.3 | 0 | -110 | Down | Down |
| balance of trade | ng.balanceoftrade | 2158250.7 | 1835120 | 18 | 138 | UP | UP |
| imports | ng.imports | 4104729.0 | 4822310 | -15 | 120 | UP | UP |
| exports | ng.exports | 4284566.61 | 4267980 | 0 | 123 | UP | UP |
| external debt | ng.externaldebt | 41594.52 | 43159.2 | -4 | 30 | UP | UP |
| foreign exchange reserves | ng.fxreserves | 34070.0 | 32690 | 4 | -0 | UP | Down |
| gold reserves | ng.goldres | 21.37 | 21.37 | 0 | -0 | Down | Down |