France Economy & France Markets Data analytics
MacroVar monitors real-time economic, financial and geopolitical developments for the France economy and France markets by analyzing financial, economic data and real-time news using statistical models. To help you forecast and analyze economic and financial developments, our team provides you with explanations of the theory and structure of our models and access to financial and economic data.
France Overview
France Overview presents the current trends and dynamics of the major France financial markets and economic indicators. Select Details to get more information for each indicator, use Factors to monitor current statistical analysis of financial & economic factors affecting the specific asset, and select research to read the latest MacroVar research for the specific asset/indicator.
| Price | 1D% | M | T | B | Factors | Research | Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAC 40 | 7573.55 | 0.86 | -0.04 | 2.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| France 2-year bond yield | 3.07 | -2.26 | -0.02 | -8.87 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FOAT France 10Y Bonds | 124.07 | -0.11 | 0 | -3.29 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| France 10-Year Bond Yield | 3.18 | -1.85 | 0.01 | 8.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing PMI | 45.3 | -2 | -2 | -2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Services PMI | 48.8 | -1 | -1 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ESI - Economic Composite | 97.3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Price | 1D% | M | T | B | Factors | Research | Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAC 40 | 7573.55 | 0.86 | -0.04 | 2.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| France ETF | 38.63 | 1.23 | -0.06 | 2.99 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| France 2-year bond yield | 3.07 | -2.26 | -0.02 | -8.87 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FOAT France 10Y Bonds | 124.07 | -0.11 | 0 | -3.29 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| France 10-Year Bond Yield | 3.18 | -1.85 | 0.01 | 8.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| France Yield Curve | 0.17 | 30.84 | 1.62 | -170.36 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| France Credit Default Swaps | 28.32 | 0 | 36.73 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Price | 1D% | M | T | B | Factors | Research | Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composite PMI | 48.8 | 0 | 0 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ESI - Economic Composite | 97.3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing PMI | 45.3 | -2 | -2 | -2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Services PMI | 48.8 | -1 | -1 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GDP Growth (annual) | 1.1 | 38 | 38 | -94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inflation CPI | 2.2 | -4 | -4 | -55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unemployment rate | 7.5 | 0 | 0 | -7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Price | 1D% | M | T | B | Factors | Research | Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAC 40 | 7573.55 | 0.86 | -0.04 | 2.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| France 2-year bond yield | 3.07 | -2.26 | -0.02 | -8.87 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FOAT France 10Y Bonds | 124.07 | -0.11 | 0 | -3.29 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| France 10-Year Bond Yield | 3.18 | -1.85 | 0.01 | 8.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| France Credit Default Swaps | 28.32 | 0 | 36.73 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
France Market News
| Time | Headlines | |
|---|---|---|
| 2024-07-04 08:44 | German Industrial Orders MoM Actual -1.6% (Forecast 0.5%, Previous -0.2%) | |
| 2024-07-02 05:40 | Treasuries Are Hit as US election risks come into focus - US Market Wrap | |
| 2024-07-02 05:40 | ECB's President Lagarde: It will take time to be certain that inflation is on track. | |
| 2024-07-02 05:40 | ECB's President Lagarde: A strong labour market means we have time to gather information. | |
| 2024-07-02 05:40 | ECB's President Lagarde: The strong labor market allows the ECB to gather enough data. | |
| 2024-07-02 05:40 | ECB's President Lagarde: A soft landing for the euro zone economy is not guaranteed. | |
| 2024-07-02 05:40 | ECB's Wunsch: I would need convincing to cut more than twice this year. | |
| 2024-07-02 05:40 | ECB's Wunsch: We would need convincing to cut more than twice this year. | |
| 2024-07-02 05:40 | ECB's Wunsch: Market pricing on the ECB rate path looks reasonable. | |
| 2024-07-02 05:40 | ECB's Simkus: We shouldn't limit rate moves to projection meetings. | |
France Economic Sectors
MacroVar analyzes in detail the dynamics of the France economy by economic sector and subsector based on data obtained from Eurostat. MacroVar presents for free current dynamics of France economic sectors.
| Sectors | Last | Previous | Trend | Momentum | Trend | MoM% | QoQ% | YoY% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Economic Conditions | 97.2 | 97.9 | 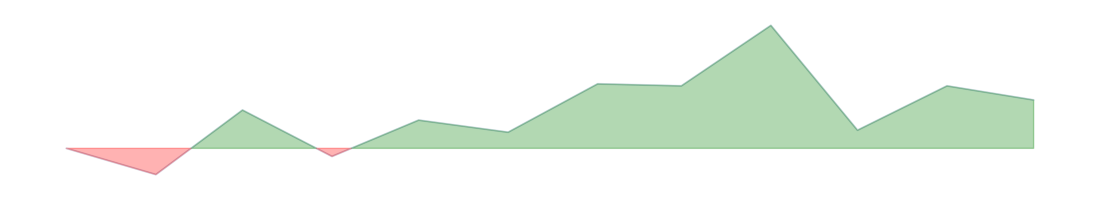 | -1 | -4 | 0 | ||
| Manufacturing sector | -7.9 | -8.9 | 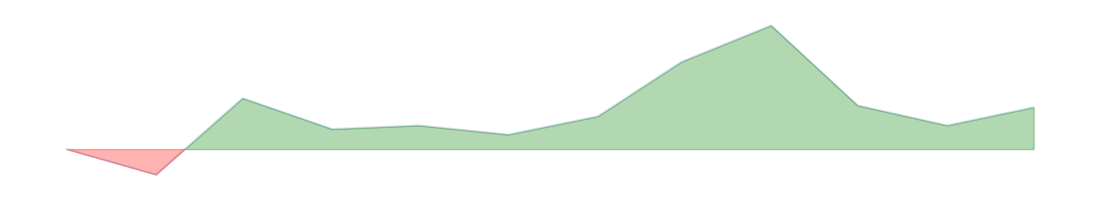 | -11 | 132 | 5 | ||
| Services sector | -1.1 | 1.8 | 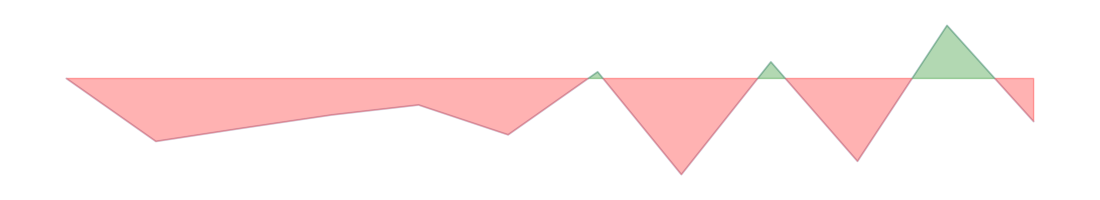 | -161 | -257 | -222 | ||
| Retail sector | -12.7 | -10.5 | 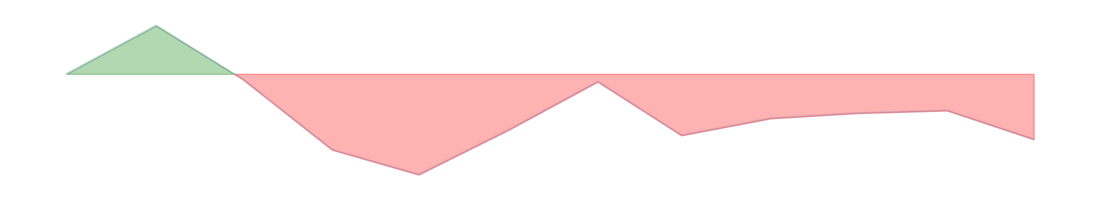 | 21 | 14 | 15 | ||
| Consumer sector | -14.5 | -13.8 | 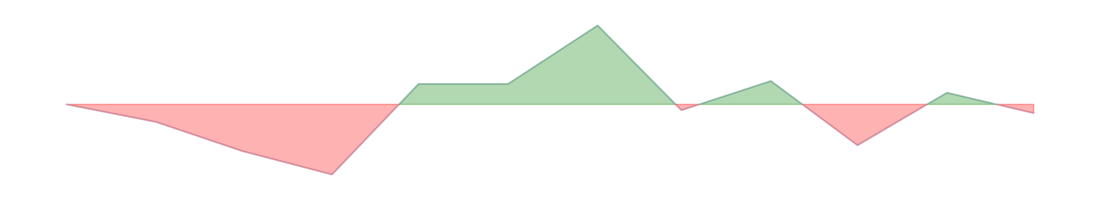 | 5 | 8 | -2 | ||
| Construction sector | -8.5 | -9.5 | 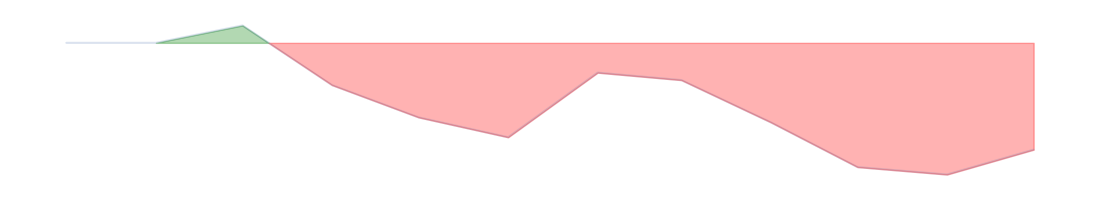 | -11 | 15 | 204 | ||
| Employment dynamics | 97.7 | 98.1 |  | -0 | 0 | -5 |
France's detailed economic sector analysis by subsectors and industries is only available to Premium users.
Upgrade your membership to get access
Upgrade your membership to get access
Check Subsector analysis details
France Economic Calendar
Economic calendar presents real-time updates for actual, forecasts and consensus values of economic indicators and updates related to the France economy.
| Time | Imp | Event | Actual | Forecast | Previous |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 09:45 | French Consumer Confidence | 91 | 90 | 89 | |
| 11:00 | ECB 1 Year CPI Expectations | 2.8% | - | 2.8% | |
| 11:00 | ECB 3 Year CPI Expectations | 2.3% | - | 2.3% |
France Economic Overview
France economic overview presents a snapshot of US current economic conditions. You can find details for the France economy subsections by exploring the sections below.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composite PMI | fr.comppmi | 48.8 | 48.9 | -0 | 3 | UP | UP |
| ESI - Economic Composite | fr.esi.conf | 97.2 | 97.9 | -1 | 0 | UP | UP |
| Industrial New Orders | fr.man.orders | -16.6 | -17.6 | -6 | -17 | UP | UP |
| Industrial Prices | fr.man.priceexp | 0.6 | 3.2 | -81 | -81 | Down | Down |
| Manufacturing PMI | fr.manpmi | 44.1 | 45.4 | -3 | -2 | Down | Down |
| Industrial Confidence | fr.esi.man | -7.9 | -8.9 | -11 | 5 | UP | Down |
| services pmi | fr.servpmi | 50.7 | 49.6 | 2 | 8 | UP | UP |
| Services Confidence | fr.esi.serv | -1.1 | 1.8 | -161 | -222 | Down | Down |
| Consumer Confidence | fr.esi.cons | -14.5 | -13.8 | 5 | -2 | Down | UP |
| Retail Confidence | fr.esi.ret | -12.7 | -10.5 | 21 | 15 | Down | Down |
| construction pmi | fr.constrpmi | 41.0 | 43.4 | -6 | -6 | Down | Down |
| Construction Confidence | fr.esi.constr | -8.5 | -9.5 | -11 | 204 | Down | Down |
France Manufacturing
MacroVar tracks hundreds of indicators related to France manufacturing sector.
| 1Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing PMI | fr.manpmi | 44.1 | 45.4 | -3 | -2 | Down | Down |
| industrial production | fr.indproduction | -3.07 | 1.07 | -387 | -263 | Down | Down |
France Services
MacroVar tracks hundreds of indicators related to France services sector.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| services pmi | fr.servpmi | 50.7 | 49.6 | 2 | 8 | UP | UP |
France consumer sentiment
Consumer spending makes a large part of the France Economy.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| consumer confidence | fr.consconfidence | 91.0 | 90s | 1 | 7 | UP | UP |
| Consumer Confidence | fr.esi.cons | -14.5 | -13.8s | 5 | -2 | Down | UP |
| Employment Dynamics | fr.eei.emp | 97.7 | 98.1s | -0 | -5 | Down | Down |
| unemployment rate | fr.unemploymentrate | 7.5 | 7.5s | 0 | -7 | UP | Down |
| retail sales | fr.retailsalesan | -1.4 | -0.2s | 600 | -63 | UP | UP |
| retail sales MoM | fr.retailsales | -0.4 | -0.4s | 0 | 300 | Down | Down |
| car registrations | fr.carregistrations | 181712.0 | 141298s | 29 | -5 | UP | Down |
| building permits | fr.buildingpermits | 27587.0 | 29414s | -6 | -19 | Down | Down |
France Construction
The France construction sector is a significant component of the France economy. MacroVar monitors leading indicators of construction activity like building permits and new home sales.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| building permits | fr.buildingpermits | 27587.0 | 29414 | -6 | -19 | Down | Down |
| housing starts | fr.housingstarts | 23454.0 | 21861 | 7 | -3 | UP | Down |
| new home sales | fr.newhomesales | 15131.0 | 15701 | -4 | -52 | Down | Down |
France Macroeconomic outlook
France Macroeconomic outlook presents an overview of the long-term fundamental coincident factors of the France economy. Components monitored are the country's rserves, debt, Monetary Policy and Fiscal Policy. Explore France macroeconomic model in detail.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gdp | fr.gdp | 3030.9 | 2782.91 | 9 | 6 | UP | UP |
| Real GDP | fr.realgdp | 595694.0 | 594336 | 0 | 7 | UP | UP |
| gdp growth annual | fr.gdpgrowthan | 1.1 | 0.8 | 38 | -94 | Down | Down |
| gdp growth | fr.gdpgrowth | 0.2 | 0.1 | 100 | -80 | Down | Down |
| inflation cpi | fr.inflationcpi | 2.2 | 2.3 | -4 | -55 | Down | Down |
| interest rate | fr.interestrate | 4.5 | 4.5 | 0 | 8900 | UP | UP |
| unemployment rate | fr.unemploymentrate | 7.5 | 7.5 | 0 | -7 | UP | Down |
| government debt | fr.govdebt | 3101.2 | 3093.1 | 0 | 17 | UP | UP |
| external debt | fr.externaldebt | 6916335.0 | 7003750 | -1 | 15 | UP | UP |
| government debt to gdp | fr.govdebtgdp | 110.6 | 111.9 | -1 | 26 | UP | UP |
| current account | fr.currentaccount | -1818.0 | 614 | -396 | 56 | Down | Down |
| current account to gdp | fr.currentaccountgdp | -0.7 | -2 | -65 | -22 | UP | UP |
| exports | fr.exports | 50200.0 | 51100 | -2 | -5 | Down | Down |
| imports | fr.imports | 58200.0 | 58600 | -1 | -4 | UP | Down |
| foreign exchange reserves | fr.fxreserves | 248.11 | 245.9 | 1 | 17 | UP | UP |
| gold reserves | fr.goldres | 2436.97 | 2436.97 | 0 | 0 | UP | UP |
| government revenues | fr.govrev | 129.58 | 74.4 | 74 | 1 | Down | UP |
| fiscal expenditure | fr.fiscalexp | 221.75 | 153.52 | 44 | 2 | Down | UP |
France Inflation
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| inflation cpi | fr.inflationcpi | 2.2 | 2.3 | -4 | -55 | Down | Down |
| core inflation rate | fr.coreinflationrate | 1.8 | 1.7 | 6 | -68 | Down | Down |
| Produce Prices YoY | fr.producerpricesch | -6.7 | -6.7 | 0 | -316 | Down | Down |
France Employment
MacroVar monitors leading indicators (ESI employment activity) and lagging indicators of France employment. France employment is one of the major factors affecting ECB monetary policy.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unemployment rate | fr.unemploymentrate | 7.5 | 7.5 | 0 | -7 | UP | Down |
France Monetary Policy
France Monetary policy is monitored by tracking the most important indicators related to the central bank's balance sheet and interest rates.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| interest rate | fr.interestrate | 4.5 | 4.5 | 0 | 8900 | UP | UP |
| central bank balance sheet | fr.cb.assets | 1530170.0 | 1543340 | -1 | -14 | Down | Down |
| banks balance sheet | fr.banks.bs | 12221383.0 | 12289900 | -1 | 2 | UP | UP |
| money supply m1 | fr.msm1 | 1584798.0 | 1593160 | -1 | -7 | Down | Down |
| money supply m2 | fr.msm2 | 2985366.0 | 2992820 | -0 | -0 | Down | Down |
| government debt to gdp | fr.govdebtgdp | 110.6 | 111.9 | -1 | 26 | UP | UP |
| loan growth | fr.loangrowth | -1.28 | -0.57 | 125 | -128 | Down | Down |
| loans to private sector | fr.loanprivate | 3073224.0 | 3066810 | 0 | 0 | UP | UP |
| France Credit Rating (S&P) | RATING.S&P.FR | ||||||
| France Credit Rating (Moody's) | RATING.MOODYS.FR | ||||||
| France Credit Rating (Fitch) | RATING.FITCH.FR |
France Fiscal Policy
France Fiscal policy is monitored by tracking the most important indicators related to the Treasury's decisions on government spending, revenues and budget surplus/deficit.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| government revenues | fr.govrev | 129.58 | 74.4 | 74 | 1 | Down | UP |
| fiscal expenditure | fr.fiscalexp | 221.75 | 153.52 | 44 | 2 | Down | UP |
| government budget | fr.govbudget | -5.5 | -4.8 | 15 | 6 | Down | Down |
| Government budget | fr.govbudgetvalue | -113.5 | -91.6 | 24 | 6 | UP | Down |
| government debt | fr.govdebt | 3101.2 | 3093.1 | 0 | 17 | UP | UP |
| government debt to gdp | fr.govdebtgdp | 110.6 | 111.9 | -1 | 26 | UP | UP |
France Trade
France trade activity is monitored by tracking Trade and Capital flows.
| Indicator | Symbol | Actual | Previous | M/M% | Y/Y% | Trend | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current account | fr.currentaccount | -1818.0 | 614 | -396 | 56 | Down | Down |
| current account to gdp | fr.currentaccountgdp | -0.7 | -2 | -65 | -22 | UP | UP |
| balance of trade | fr.balanceoftrade | -8000.0 | -7500 | 7 | 1 | Down | Down |
| imports | fr.imports | 58200.0 | 58600 | -1 | -4 | UP | Down |
| exports | fr.exports | 50200.0 | 51100 | -2 | -5 | Down | Down |
| capital flows | fr.capitalflows | -21739.0 | -6586 | 230 | 43 | Down | Down |
| foreign direct investment | fr.fdi | -103.0 | -1003 | -90 | -127 | Down | Down |
| external debt | fr.externaldebt | 6916335.0 | 7003750 | -1 | 15 | UP | UP |
| foreign exchange reserves | fr.fxreserves | 248.11 | 245.9 | 1 | 17 | UP | UP |
| gold reserves | fr.goldres | 2436.97 | 2436.97 | 0 | 0 | UP | UP |